December 31, 2019
How to Prepare for a Design Direction Challenge

DURATION
10 mincategories
Tags
share
Design Direction is a new type of challenge, in which the goal is to quickly create design guidance and concepts for the customer’s project. The goal of “Design Direction” is to not create high-fidelity designs but to focus on thinking through the problem and proposing a direction for the project. Design Direction is a little bit of Information Architecture, a little bit of UI/UX design work to help inspire the customer and to inspire a future designer of the idea, product, or app. The concept delivered by the client is a form of wireframe presentation that is not super low fidelity but is also not a finished design product.
This challenge usually lasts 48 hours+. Based on the design sprint, carried out by the customer, the designers are asked to propose features and put together high-level information and visual direction which will be used as input into a future UI challenge. In this article, I will explain what knowledge you need to have to participate in design direction challenges.
ARTIFACTS DESIGN DIRECTION
In the design direction challenge, we will be given artifacts from the sprint design process or the customer’s workshops/meetings. To create a good submission in accordance with the wishes of the client and user, it is important for you to understand the requirements well. Some of the artifacts that are usually given in the design direction include:
Affinity Diagrams

Affinity diagrams are tools usually used by clients to conduct brainstorming sessions for the formation of a user story that will be developed into a feature of product design in the future.
Usually, affinity diagrams are shaped like sticky notes stacked in groups from large pile groups (initial brainstorming sessions) to small groups (problem extraction process and user mandatory). The following is an example of applying an affinity diagram to break down a problem to become a mandatory design/user story.
1. The Problem
Let us raise a problem that we are tasked with creating applications to help people in developing countries who want to use public transportation.
2. Interview with Users
For the interview, we assume that we and colleagues have interviewed users with various backgrounds and have experience using public transportation.
3. Brainstorming Process
The brainstorming process ensued. Your coworkers put their thoughts on the specified board and found the following results.
4. Sorting the problem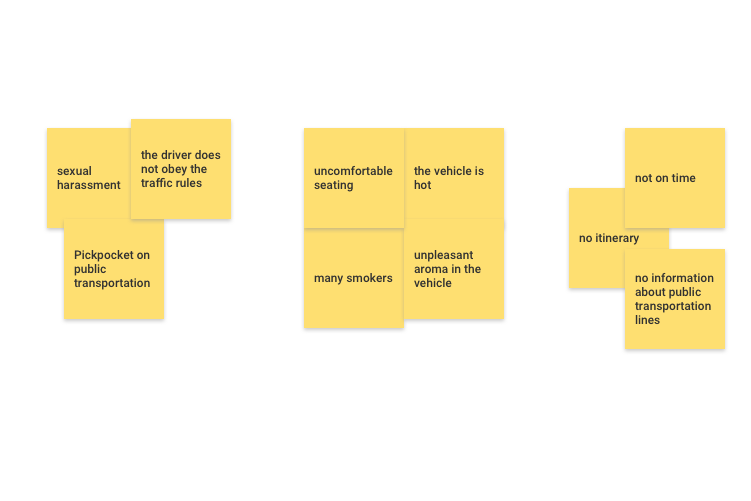
Next, let’s collect post-it notes and sticky notes that have the same category.
5. Extraction Process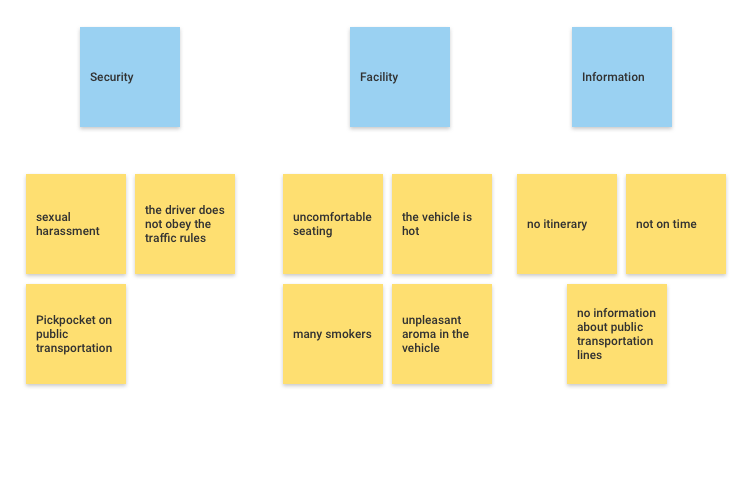
Next, let’s extract the results of categorization into one term. Make another sticky note to write down the categories of the set of problems we have categorized. In this example I used blue.
6. Design Mandatory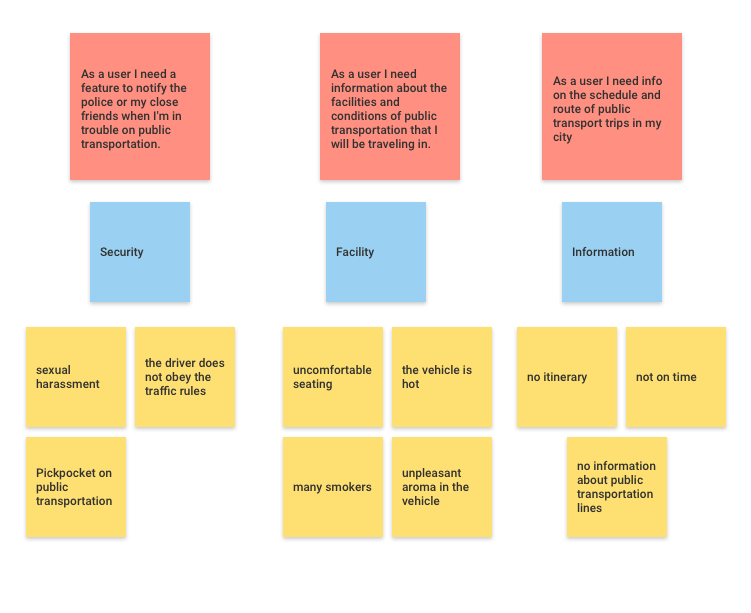
The next step is based on the categories and problems that are collected, let’s arrange it into one or more design mandatory or user stories. I use red sticky notes to write user stories or designs mandatory.
User profiles / User Persona

Source: Ofer Ariel
User profiles or persona are the results of the analysis of the sprint design process which contains a representation of the user type which will use the customer’s application. The personas help you understand the different needs and behaviors of various target users. This document is useful to direct us as designers to create an optimal user experience.
Usually, the client’s document will provide a form of a fictitious profile that contains data from user photos, description of age, identity, hobbies, habits, and preferences of the example of the intended user.
Video Presentation
Sometimes, the customer will provide a video where he will explain the user flow, the expectations from the design challenge, or any additional thoughts that might be hard to put down. Don’t forget to ask the co-pilot in the forum if you feel that the video provided has a sound or purpose that is unclear.
User Flow Diagram
Imagine you are planning to find a song in the Spotify application; the series of steps you will take are as follows:
Open the Spotify application.
Look for the “Search” icon to enter the search page.
Type the names of songs you are looking for in the search field and see the results.
Play a song from the search results.
From the example above you can see there are several steps a user has to complete to play a song. Things like this are one part of the Spotify application user flow diagram.
A user flow diagram outlines the steps the user will take in carrying out a task or feature. In the design direction challenge the client will usually give a brief in the form of mapping or wireframe about how the user will interact with the application / website design (find your website address from search engines, referrals, social media) and show the stages of the user accessing the features of the product to be made.
What you need to pay attention to is how to map out the flow or stages that are potentially problematic and fix them until the application / website that we build can operate more effectively. You can also learn about similar products to the products provided by clients, watch how successful visitors get what they want from competitor products, then compare with the user flow that your clients want. You can determine where the location is smooth and where errors occur. So, the user flow diagram can show you what is and isn’t going well from a visitor’s perspective.
THINGS YOUR SUBMISSION SHOULD INCLUDE
Quick Wireframes
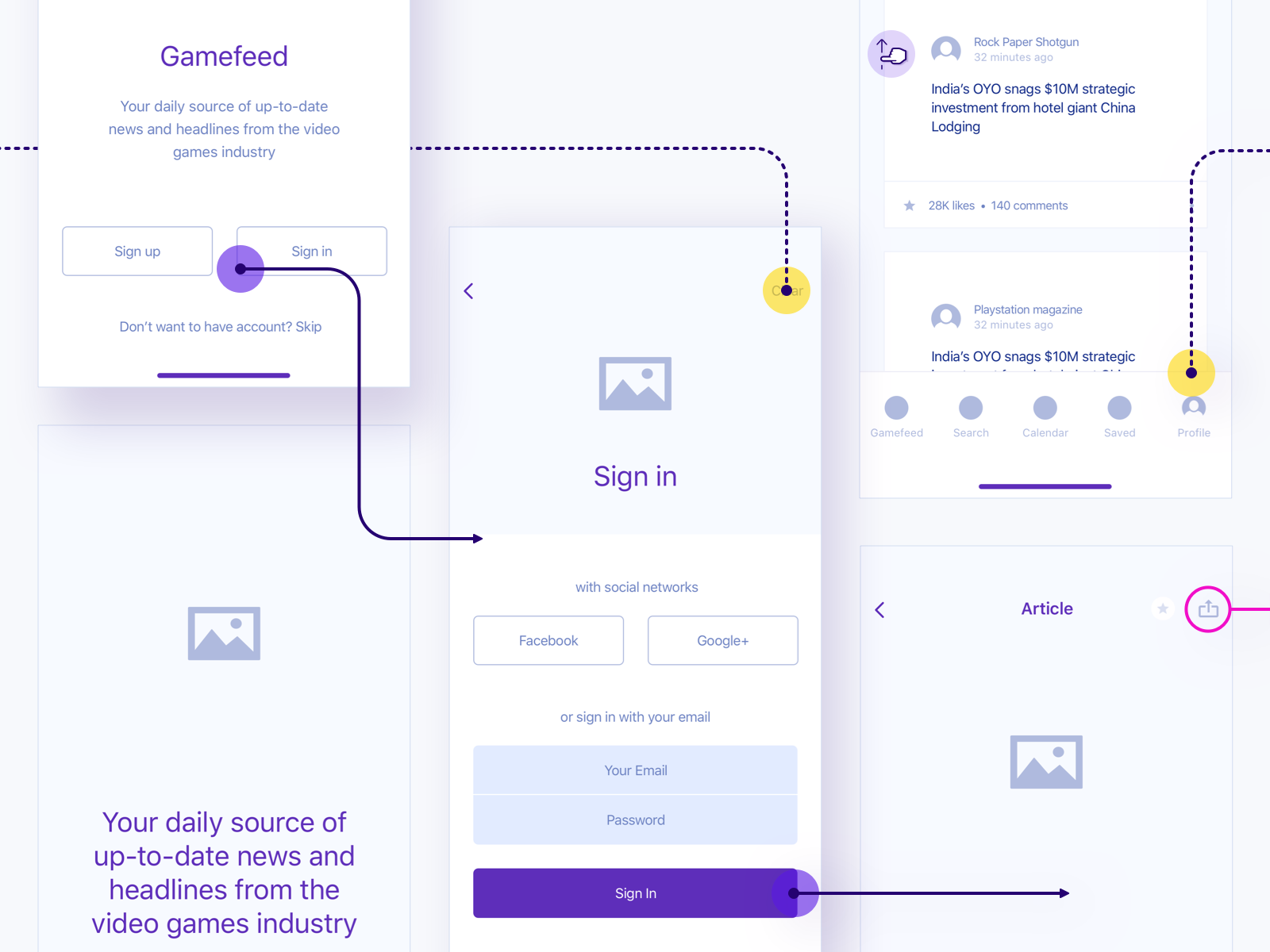
Author: Piotr Kaźmierczak
Make the right wireframe to be a guide for other designers to develop it into a complex screen. This term is often referred to as “Key Screen” which is the basic screen of a feature that can be explored by designers to develop features such as popups, filters, changing lists to grids, etc.
Make sure the wireframe that is designed describes the position of the elements of the design you are making. Don’t hesitate to add info or a description of the wireframe screen that you created to help the customer understand the reasoning behind your solution. The wireframes are important to show where we want the project to go as a direction but they should not be full-fledged wireframes.
Design Guidelines

Author: Ramotion
The design directives are guidelines that will later be used by other designers to create more complex application designs and other future development of products. The design guide contains recommendations for color palettes, family fonts and sizes, the use of icons, and what photo styles to use in the design. Make a design guide that can provide recommendations on how to achieve the design principles in accordance with the wishes of the client and their application that supports cross-platform design.
The Vision of the Application
Author: Ramotion
A product is usually born from an idea. The ideas obtained arise from existing problems. Now from the existing problems, look for a solution to solve the problem. In order for other designers to understand the main problems and solutions to be solved, it is necessary for us to design direction makers to create a description of the application’s vision. Don’t forget to place it at the beginning of the design presentation. Also, include illustrations/images that can describe the purpose of the application or product being developed.
Sitemaps
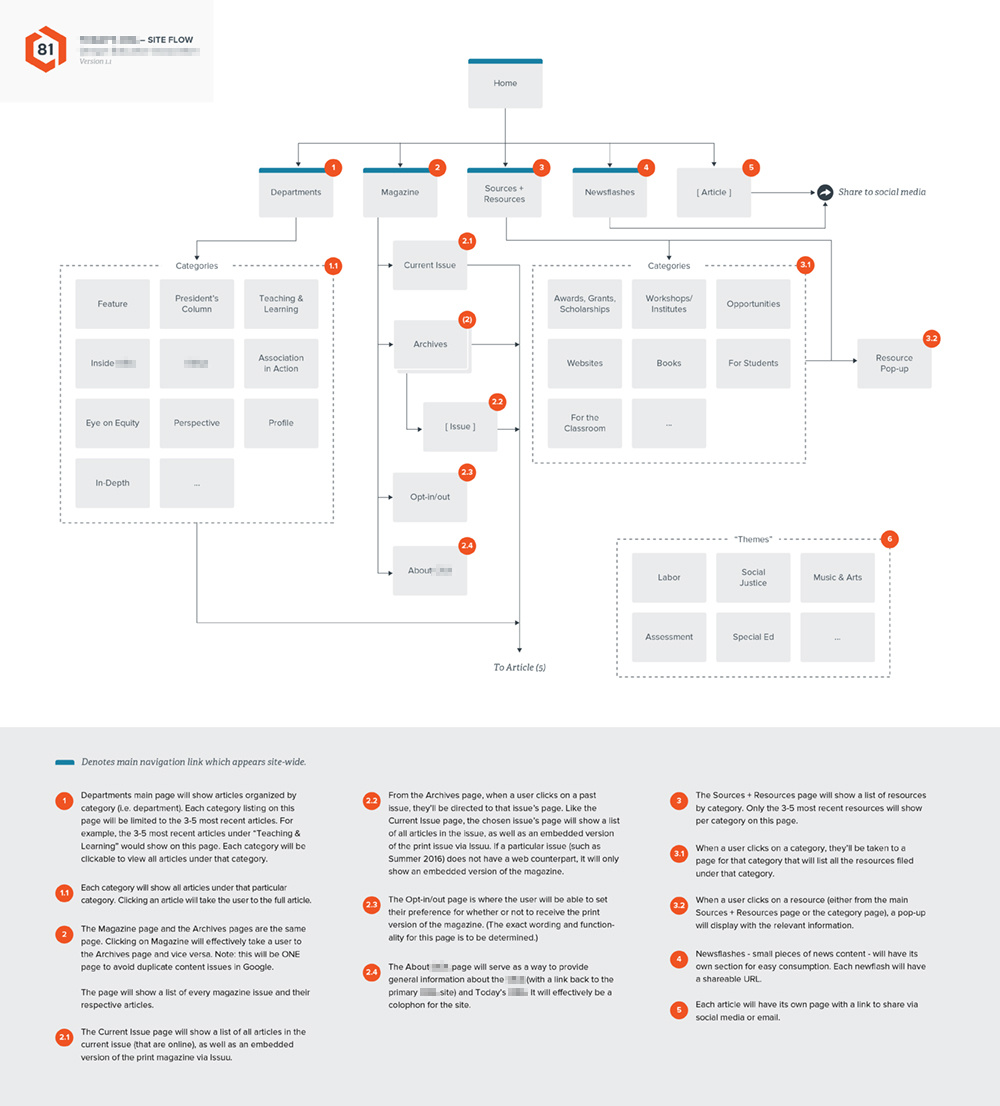
Author: Angie Herrera
Sitemaps are the structure of the product that you are designing. A sitemap is usually shaped like a basic diagram that illustrates the application hierarchy or the flow of movement from one page/feature to another page/feature.
Mockup & Design Presentation
Author: Ramotion
Apart from creating a good design and guidance system, don’t forget to add a good presentation. Use a mockup design for presentations to make them look more original. You can take it free from the internet. But don’t forget to choose those who have a CC license and declared it in the contest notes file.